
How US Startups Use Press Releases to Get Featured on Google News

About Author
Recent post
Why US Businesses Lose Rankings Due to Incorrect Citations
Why Some US Websites Rank Faster Than Others
Local Press Releases in the USA: City-Level PR That Actually Ranks
Guest Posting for US Local Businesses (City & State Targeting)
Categories
Press release marketing has changed quietly for US startups. It’s no longer treated as a link tactic or a one-time announcement tool. Instead, it’s increasingly evaluated as a credibility and discovery signal, especially for brands aiming to appear in Google News and other trusted surfaces.
What confuses many startup teams is that press releases still look the same on the surface. The format hasn’t shifted dramatically. Distribution options still exist. Writing services still promise reach. Yet outcomes vary widely. Some startups earn recurring visibility and media trust. Others see releases disappear without impact.
The difference isn’t the budget. It’s intent alignment.
Startups that succeed with press release marketing understand how Google News evaluates stories, how editors filter submissions, and how credibility is inferred before amplification occurs. They question why a release should exist, not just how it should be written or distributed.
This blog explores how US startups use press releases strategically to earn Google News visibility, what press release marketing actually signals today, and why execution decisions around format, proof, and intent determine whether PR becomes a growth asset or a quiet failure.
Local SEO Foundations US Businesses Cannot Skip
Local SEO for US businesses is interpreted as an identity layer first. Search engines map a business as a real entity tied to operational geography. Offline recall seeds digital demand clusters. These clusters validate legitimacy quietly over time. This section stays separate from citation and press release logic.
1. Local Trust Starts Before Digital Discovery
Local SEO in the US is influenced long before ranking tools are applied. Search engines study businesses only after users already recognize them in a region. Recognition comes from service reliability and repeated neighborhood recommendations. US service brands build recall by serving the same counties and ZIP clusters consistently. When users hear a brand name offline, they search it later with city or service intent.
Engines treat repeated same-region brand searches as authenticity evidence. Authenticity is inferred from behavior, not formatting tricks. If 200 people in one county search the same brand in 10 days, engines open ranking pools faster. But opening pools means eligibility, not rank order. Eligibility always comes first. Order is tested later.
2. Community Reputation Becomes a Data Source
Search engines ingest offline reputation like a secondary data layer. This includes local service logs, vendor networks, and repeat booking histories. Many US home service brands naturally enter offline ecosystems like apartment boards and contractor alliances. These ecosystems generate service records. Records create continuity graphs for engines to evaluate.
Continuity is a ranking stabilizer. Stability reduces entity re-testing cycles. When cycles drop, authority compounding begins. Compounding fails when reputation nodes look fragmented. Fragmented nodes delay graph merging. Graph merging must happen before consistent local visibility grows. Visibility improves when engines stop questioning geography shifts and category noise. Noise increases recalibration. Recalibration slows compounding.
3. Branded Regional Search Clusters as Legitimacy Proof
Search engines form behavioral polygons from repeated branded regional queries. These polygons act as implicit service jurisdiction maps. If 500 users from three connected counties search the same brand with intent, the polygon strengthens. Strong polygons reduce ambiguity. Ambiguity is the biggest silent blocker in local ranking.
Blockers trigger repeated category reassignment. Reassignment resets confidence loops. Confidence loops must stay intact for compounding to occur. US businesses that rank steadily passed ambiguity filters early. Filters are cleared through human query repetition math. Math means repeat rate, geography coherence and same-region ratios. Same-region ratios always outperform scattered geography claims.
4. Demand Patterns Outweigh URL Authority
US local search evaluates expectation-based queries before backlinks or URLs. Expectation-based queries mean users already believe the business serves their zone. This belief comes from offline recall loops. Engines measure query repetition like legitimacy scoring. Scoring is binary early on. Binary means verified or unverified.
Unverified entities are tested by human demand recurrence, not links first. Recurrence qualifies the entity for local ranking pools. Pools then test ranking order. Order cannot repair identity ambiguity later. Order works only after legitimacy is inferred. Inference is based on query clusters, not distribution claims. This section speaks only about demand behavior. It excludes citation frameworks from your blog.
5. Offline Authority Creates Natural Digital Gravity =
Digital gravity means voluntary mentions from users, reviewers, and local partners. Voluntary mentions are stronger when they follow recall, not incentives. US businesses see higher review cadence when recall exists first. Cadence means steady arrival, not bursts. Bursts look synthetic. Steady looks operational.
Mention velocity is mapped into sentiment clusters. Positive sentiment improves review and engagement ratios later. Ratios influence ranking stability. Stability drives compounding authority quietly. Quiet compounding beats fast spikes. Spikes fade. Loops compound. Local SEO rewards loops, not noise.
Why Press Release Marketing Fails for Startups
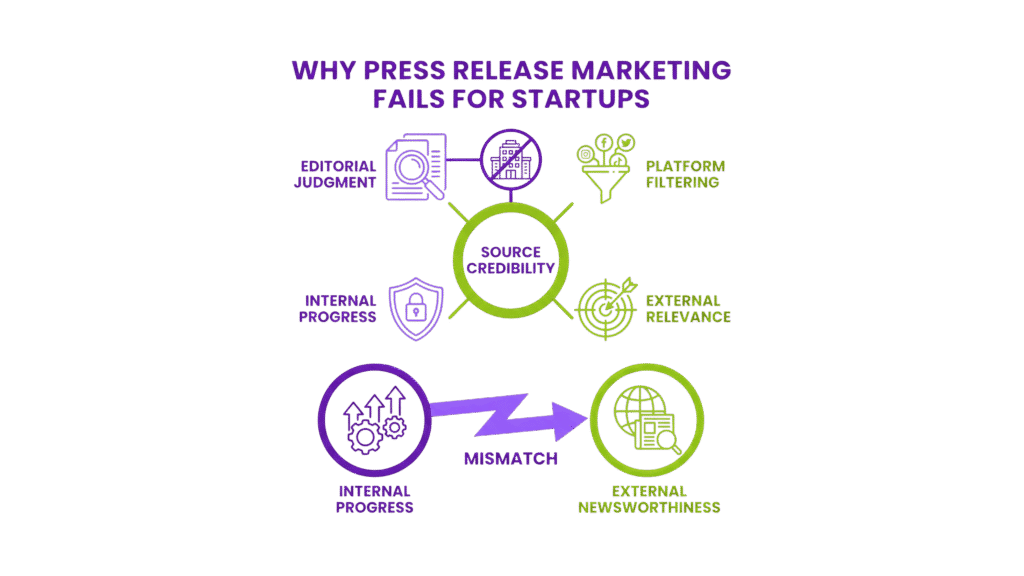
Press release marketing sits at an intersection where editorial judgment, platform filtering, and source credibility meet. For startups, this intersection is often misunderstood. Many assume that accuracy, clarity, and momentum naturally translate into attention. In reality, editorial systems interpret early-stage signals through a different lens, one shaped by risk management and external relevance rather than internal progress.
When outcomes fall short, the issue is rarely effort or intent. It is more often a mismatch between how startups communicate progress and how editors define newsworthiness.
Announcements Are Judged by External Impact
The first friction point appears when internal milestones are framed as news. Product launches, feature updates, early traction, or funding rounds represent meaningful progress inside the company. Editors, however, assess whether anything has changed outside the organisation.
Newsworthiness is defined by consequence. Editors look for shifts in user behaviour, market dynamics, or shared understanding. When that external impact is unclear, a release stalls before writing quality becomes relevant. Accuracy is not questioned. Relevance is.
Distribution Is Interpreted as Exposure, Not Validation
Startups often rely on distribution to signal importance. Broader reach is assumed to increase legitimacy. In practice, distribution determines exposure, not significance. Without a clear editorial frame, wide distribution communicates broadcast intent rather than urgency.
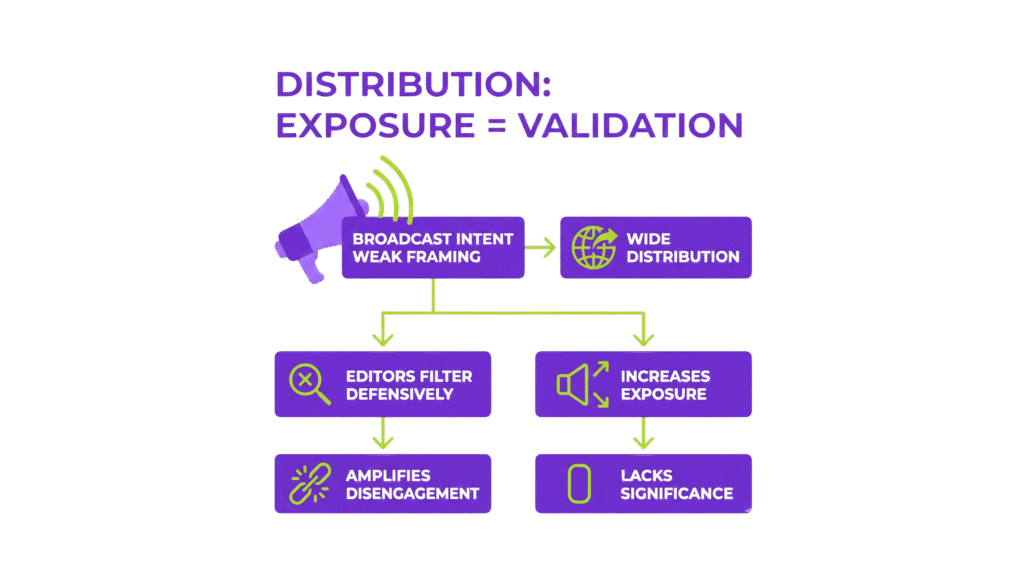
Editors are trained to filter broadcast signals defensively. When framing is weak, amplification accelerates disengagement instead of correcting it.
Verification Signals Carry More Weight Than Writing Quality
Writing quality is frequently prioritised in the hope that polish will compensate for uncertainty. Editors do not screen releases for eloquence first. They screen for verifiability. They look for signals that claims can be checked, contextualised, or corroborated without friction.
Polish without structure raises skepticism. Accuracy survives fact-checking. Credibility must survive the first read.
How US Startups Use Press Releases to Get Featured on Google News
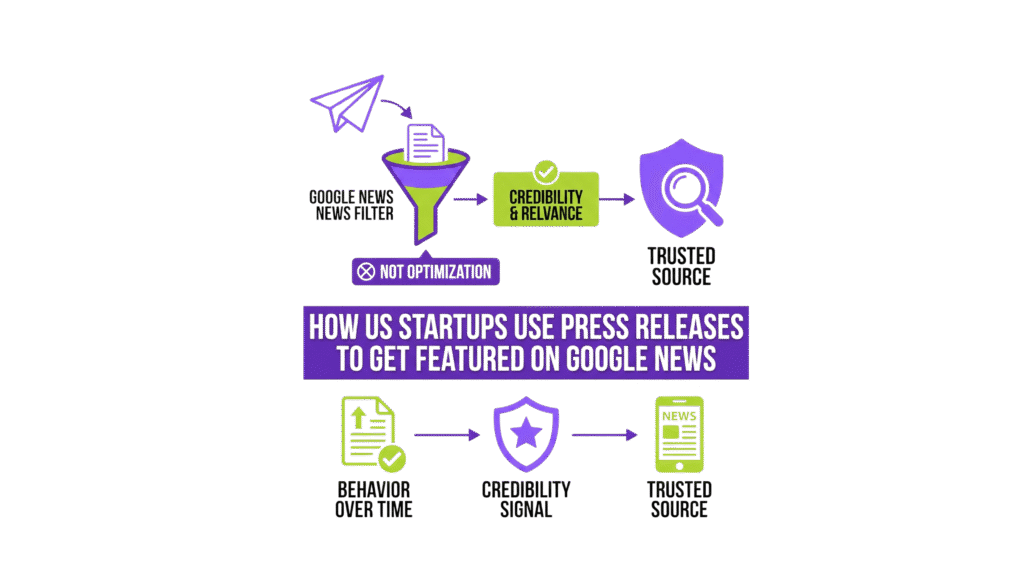
Google News does not function like traditional web search. It was not designed to reward optimisation, nor to surface every piece of distributed content that looks news-like. Instead, it operates as a filtering system, built to manage credibility, relevance, and editorial risk at scale. Within this environment, press releases are not treated as marketing assets. They are interpreted as information signals whose value depends on how they behave over time.
Understanding this distinction is critical, because many assumptions carried over from press release SEO or general press release marketing simply do not apply inside news surfaces.
Google News Prioritises Newsworthiness Over Optimisation
At its core, Google News is designed to surface stories that resemble journalism, not promotion. This does not mean press releases are excluded by default. It means they are evaluated through a different lens.
The system looks for signals that suggest a release contributes new, timely information to an ongoing narrative. Structural clarity, topical relevance, and immediacy matter far more than keyword coverage or link placement. A press release submission can be technically optimised and still fail to qualify if it does not behave like news.
In this context, optimisation is not ignored. It is simply secondary to informational value.
Source Trust Is Built Through Consistency, Not Brand Size
One of the most misunderstood aspects of Google News is how it interprets authority. Large brands do not automatically receive preferential treatment. Instead, the system evaluates source behaviour over time.
Publishing consistency, topic coherence, and historical signal quality shape trust. A smaller organisation that publishes clear, relevant, and timely releases within a defined topical space can outperform a larger brand that submits sporadic or unfocused content. Trust is accumulated through repeatable behaviour, not reputation alone.
This is why Google News feels conservative. It rewards predictability, not novelty for its own sake.
Press Releases Are Read as Signals, Not Ranking Assets
Inside Google News, press releases are not treated as tools to influence search rankings. They are treated as informational inputs. The system asks whether a release adds clarity to a topic, confirms an event, or advances a story already in motion.
This is why traditional press release SEO logic often misfires here. Links, anchors, and promotional framing carry little weight compared to signal usefulness. A release that reads like a marketing announcement may still be accurate, but accuracy alone does not make it news-relevant.
Google News evaluates what a release does, not what it points to.
Recency, Relevance & Clarity Drive Inclusion Decisions
Timeliness is a necessary but insufficient condition. Google News values recency, but only when it aligns with topical relevance. A new release disconnected from active narratives struggles to surface, regardless of freshness.
Clarity plays an equally important role. Releases that clearly state what happened, why it matters now, and where it fits within a broader context are easier for the system to interpret. Ambiguity introduces risk. Risk reduces inclusion.
This is not an editorial judgment. It is a system constraint.
Why Press Release SEO Behaves Differently in News Surfaces
press release SEO assumes that visibility is earned through crawlability, keyword alignment, and distribution breadth. Google News operates on a narrower objective. It surfaces content that behaves like credible reporting within a time-sensitive environment.
As a result, techniques that may help a release appear in web search do not translate cleanly into news visibility. The system does not reward repetition, density, or promotional language. It rewards informational efficiency.

This difference explains why press releases can rank in search but remain absent from news results.
How Repeated Low-Quality Signals Erode Trust
Google News tracks patterns, not isolated submissions. When a source repeatedly submits releases that add little informational value, trust erodes quietly. There is no penalty notice. Inclusion simply becomes less likely.
This erosion happens because the system optimises for reliability. Sources that consistently produce weak signals increase noise. Over time, the system learns to deprioritize them.
This is why Google News feels unforgiving. It remembers behaviour, not intent.
Google News evaluates press releases as part of a live information ecosystem. It prioritises newsworthiness, consistency, and clarity over optimisation and scale. Press releases are not rejected because they are promotional. They are filtered because they fail to behave like useful information.
This section explains how the system works, not how to work the system. With this foundation in place, later sections can explore how press release writing services intersect with credibility, timing, and narrative alignment — without collapsing news logic into SEO logic prematurely.
Conclusion
Press release marketing works for US startups when it’s treated as a credibility signal, not a promotional channel. Google News rewards clarity, relevance, and trust, not distribution volume or keyword alignment.
Startups that earn consistent visibility understand how platforms and editors evaluate information. They design releases to reduce doubt, fit real news cycles, and support long-term authority rather than short-term exposure.
When press releases are positioned correctly, they don’t just announce growth. They validate it.
FAQs
Why do startups still use press release marketing in 2026?
Startups use press release marketing when they need controlled visibility. A release allows them to introduce news with context, accuracy, and timing. When written well, it becomes a reference point journalists and search systems can rely on, rather than a one-off promotional push.
How has press release marketing changed for startups recently?
The shift is away from distribution volume and toward intent clarity. Startups now question why a release exists before deciding where it goes. That change matters because relevance, not reach, is what determines whether a story travels beyond the press room.
How does press release SEO actually work today?
Press release SEO works indirectly. Releases help establish entities, reinforce credibility, and support discovery signals when picked up by trusted outlets. The value comes from how the release is interpreted and reused, not from keyword placement or syndicated links.
What makes a press release news-worthy for startups?
News-worthiness comes from relevance outside the company. Funding, product updates, or partnerships matter only when framed through industry impact or user value. Startups that connect their news to a wider shift see stronger pickup and longer visibility.
How do startups decide when press release submission is worth it?
They assess timing and audience fit first. If the story aligns with current conversations and the outlet’s focus, submission makes sense. When it doesn’t, even strong distribution can feel forced and produce little return.
- Your cart is empty Browse Shop
DISCUSS NEW PROJECT OR JUST TO SAY HELLO GET IN TOUCH WITH US
info@Fastlinko.com
+91-9990725969
200 Park Home Avenue
M2R 1A2 North York, ON, Canada
© Fastlinko 2025 . All rights reserved, Rankfast







