
How to Build Citations for Service-Area Businesses With No Physical Address

About Author
Recent post
Why US Businesses Lose Rankings Due to Incorrect Citations
Why Some US Websites Rank Faster Than Others
Local Press Releases in the USA: City-Level PR That Actually Ranks
Guest Posting for US Local Businesses (City & State Targeting)
Categories
Service-area businesses (SABs) now work in a terrain where local SEO rules often break.
They rank in cities they don’t physically sit in, serve customers across fluid boundaries, and rely on trust signals that must stay clean. Local citation services do all of this, even when their addresses stay hidden. This is why search engines treat them differently.
Their footprint is behavioural, not storefront-based.
This is where citations for service-area businesses step in. Not as directory entries, but as location logic systems and references that tell Google exactly where a service business operates, how far it extends, and why its presence should matter in local results.
The challenge is that most citation sources were designed for physical storefronts. When SAB data is placed incorrectly, mismatched formats, masked addresses, and vague service zones dilute visibility.
Experts like Fastlinko specialise in SAB SEO. Competitor Local SEO citation building services also take a more forensic approach to NAP setup. They structure NAP alternatives, adjust category logic, and resurface location clarity without violating platform rules.
This blog breaks down How To Build Citations for Service-Area Businesses With No Physical Addresses
Why Service-Area Businesses Need a Different Citation Strategy
Service-area businesses (SABs) face unique challenges in local SEO.
Without a visible storefront, traditional citation logic falls short. For a proof of presence, Google requires structured context through boundaries, category alignment, and territory signals.
It focuses on all-around authentication rather than just a physical address. Understanding this difference is the key to ranking stability, multi-city visibility, and trust-building with high-intent local queries.
SABs Create an Identity Gap
Unlike storefront businesses, SABs often operate invisibly on maps and local packs.
So, Google recognises the business exists but struggles to place it accurately within a service region. This “identity gap” introduces positioning volatility, especially across competitive multi-city landscapes.
Without clearly defined territory signals, an SAB risks being invisible. Especially to relevant searches despite legitimate operations.
Masked Addresses Trigger Scrutiny
When a business hides its physical address, search engines apply additional verification logic.
Listings with incomplete or inconsistent location information face higher ranking scrutiny on SERPs. This can cause fluctuations in pack rankings, local organic results, and map visibility.
Simply blasting directories with citations without consideration for hidden addresses can amplify volatility rather than improve your brand’s visibility.
NAP Challenges Become Alternatives
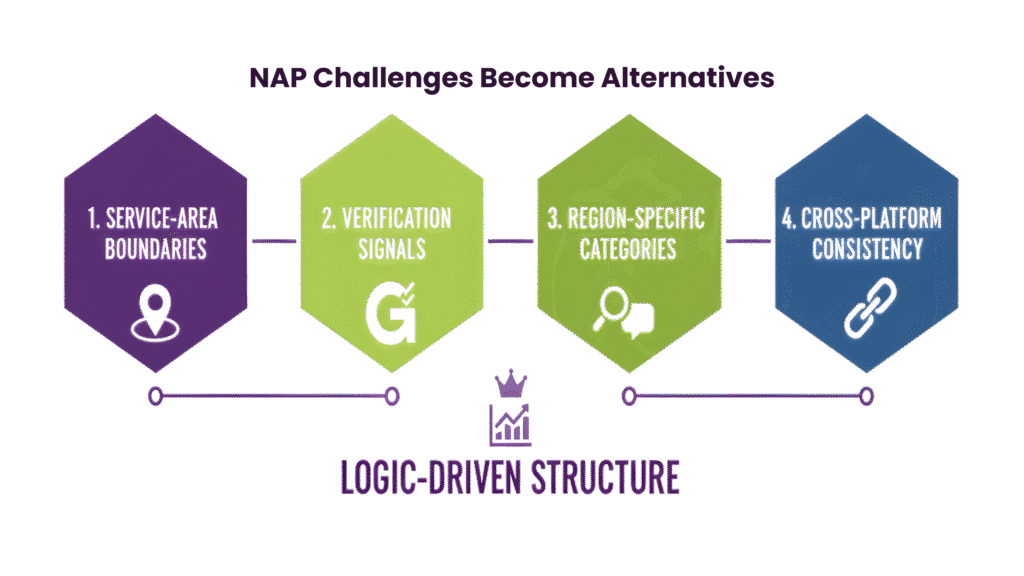
For SABs, traditional NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistency isn’t enough.
Instead, SEO specialists focus on:
- Service-area boundaries: defining operational coverage rather than a single point location.
- Verification signals: leveraging Google My Business categories, geo-verified fields, and SAB-compliant listings.
- Region-specific categories: aligning with local commercial intent and search behaviour.
- Cross-platform consistency: ensuring the same structural data appears across SAB-compatible sites.
This approach substitutes the standard NAP model with a logic-driven structure that signals operational legitimacy to search engines.
Why Directory Blasts Can Hurt Rankings
Traditional mass submissions assume businesses have visible addresses.
SABs that force this model face mismatched data, failed verification, and ranking penalties. Instead, local SEO citation building services build the context, optimising category taxonomy, radius definitions, and data-field usage for B2B brands.
This is done to reflect how Google interprets service-area operations for businesses.
How Local Citation Services Adapt
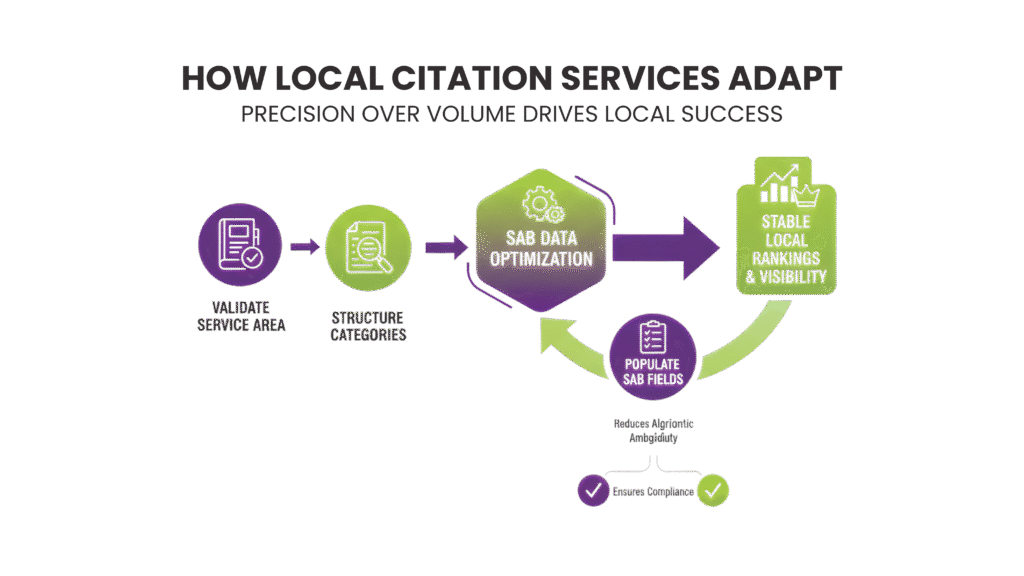
High-quality local citation services focus on precision over volume.
They validate the business’s service area, structure categories correctly, and ensure all SAB SEO fields are consistently populated. This method reduces algorithmic ambiguity.
It also positions the business across multiple regional queries without risking compliance violations or ranking swings.
Business Impact
Structured citation logic for SABs drives measurable results across the NAP setup. It also creates a strong business impact for B2B websites.
Citations for service-area businesses achieve:
- Reduced ranking volatility across maps and local packs.
- Expanded multi-city visibility without compromising verification.
- Enhanced credibility for searchers with commercial intent, boosting conversion potential.
SAB citation building is not about mass submissions.
It is an intentional exercise in location logic engineering. If done correctly, it stabilises rankings, boosts regional authority, and ensures high-intent prospects find your service exactly when and where they need it.
How Local Citation Services Validate, Structure, and Optimise SAB Data
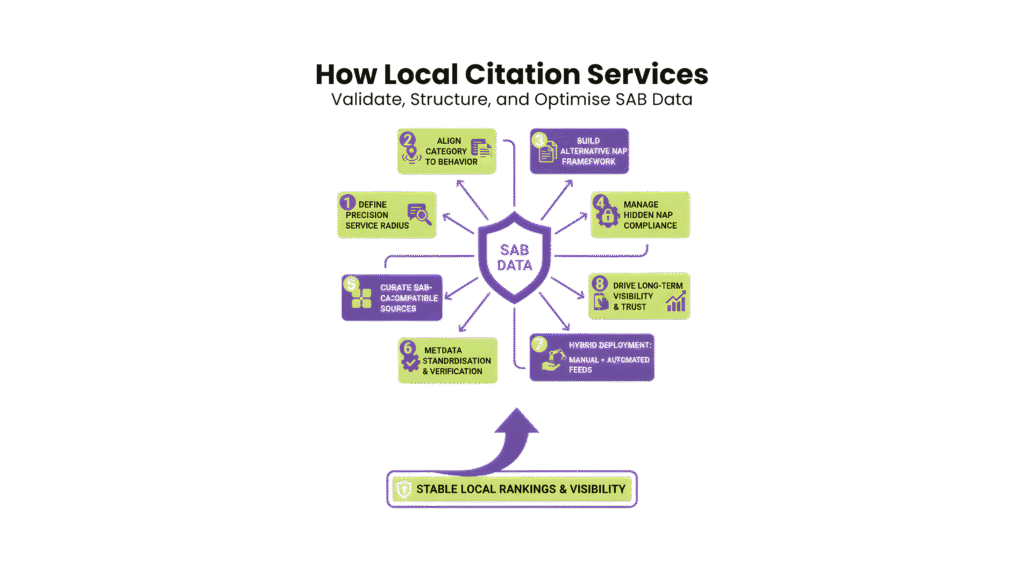
Service-area businesses (SABs) operate without a physical storefront.
This fundamentally changes how local SEO citation building services function. Traditional directory blasts and generic NAP setups fail to create trust signals for Google. They also can’t guide high-intent searchers effectively.
Leading SAB SEO experts see citation building as a structured, data-governed system that integrates geography, category relevance, and verification. Ultimately, they are able to produce stable rankings and predict local visibility.
The process of how local citation services validate structure and optimise SAB data is:
Step 1: Defining a Precision Service Radius
SAB campaigns begin with micro-level mapping of operational zones.
Each city, suburb, or ZIP-level segment is modelled based on real coverage patterns. This helps search engines connect the business to the correct local audience.
Linking to a precise service radius avoids wasted exposure in irrelevant regions, NAP setup, and SAB SEO.
It also reduces ranking volatility caused by misaligned signals.
Step 2: Category Selection Aligned to Service Behaviour
The second step is category selection based on service behaviour.
Here, Citations are categorised based on actual service behaviour and search intent instead of relying on standard storefront categories. The main task for local SEO citation building services at this stage is to analyse keyword clusters, transactional queries, and competitive taxonomies.
This ensures that category choices reflect how potential customers look for solutions. The results are compound.
It secures improved relevance in SERPs and better alignment with Google’s understanding of the business.
Step 3: Managing Hidden Address Compliance
SAB listings usually require an address suppression across major platforms.
Expert teams in citations for service-area businesses navigate complex platform rules to avoid triggering errors. Hidden address non-compliance may lead to delisting or inconsistent search visibility.
Managing hidden address compliance also includes implementing verifiable ownership credentials and service-zone boundaries. In fact, B2B brands and businesses should satisfy both algorithmic validation and platform policies.
Step 4: Building an Alternative NAP Framework
With no public address, the importance of the alternative NAP setup rises.
It channels the power of service descriptors, geo-tagged zones, verified contacts, and ownership metadata to create a robust, consistent identity. Each element upholds territorial authority.
Thus, helping search engines trust the business’s existence and reach. Even in the absence of a visible storefront.
Step 5: Curated SAB-Compatible Citation Sources
Not all citation sites support hidden addresses or SAB-specific signals.
High-level citation strategies prioritise sources that validate service territory, align with industry relevance, and provide durable indexing. Each placement is evaluated for signal quality rather than sheer volume.
Curating SAB-compatible citation sources is necessary for reducing noise and building a coherent local footprint.
Step 6: Metadata Standardisation and Verification
From hours of operation to service coverage and verification markers, metadata consistency across platforms is a priority.
It is central to reducing ranking swings. Well-structured metadata also enhances Google’s ability to associate queries with business capabilities.
In doing so, it increases local discoverability for commercial intent searches.
Step 7: Hybrid Deployment: Manual + Automated Feeds
Precision SAB citation work blends automation for scale with manual oversight for high-value or sensitive listings.
This dual approach secures accuracy and avoids duplication errors. It also allows specialists to control the category nuances and platform-specific requirements.
Step 8: Driving Long-Term Visibility and Trust
Structured citations directly influence map pack stability, local organic rankings, and trust signals.
By engineering location logic rather than relying on raw volume, SABs create a durable, algorithmically-resilient presence. They consistently signal authority to Google while guiding high-intent local traffic.
For high-net-worth operators, SAB citation building has taken a new outlook. Today, it is a disciplined exercise in geospatial intelligence, compliance, and data governance.
Proper execution transforms citations into a strategic asset. One with predictable local visibility, ranking consistency, and actionable SEO authority.
How to Build Citations for Service-Area Businesses With No Physical Address
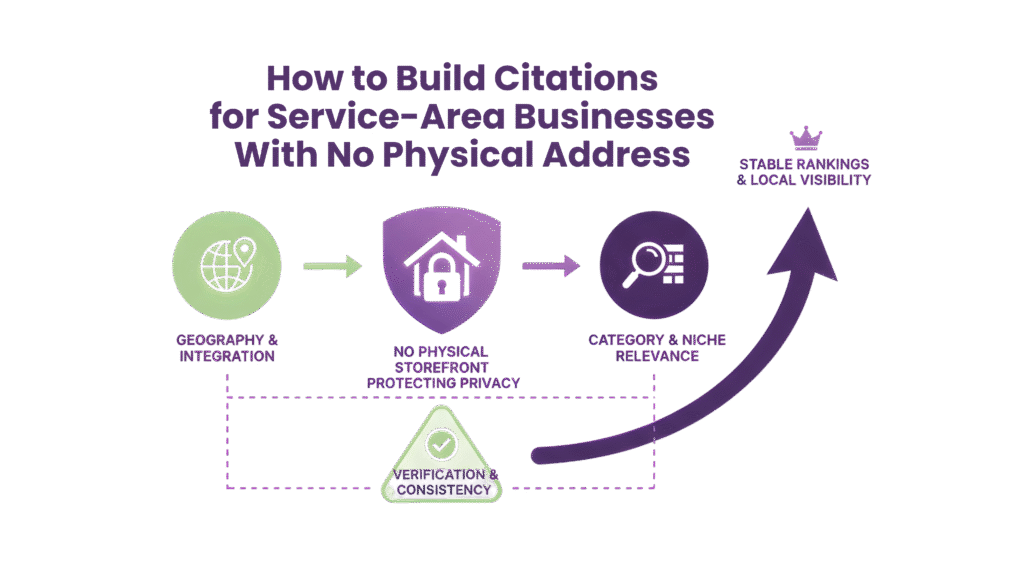
For service-area businesses (SABs), local visibility is the lifeblood.
Without a physical storefront, traditional citation approaches can backfire. In 2025, clean, structured, and territory-aware citations are essential for ranking in local packs.
This guide unpacks how to build citations for service-area businesses while maximising local SEO impact.
A. Select SAB-Compatible Citation Platforms
Not all directories treat service-area businesses equally.
Some demand a public address, risking suspension or listing penalties. Local SEO citation building services prioritise SAB-friendly platforms. These directories allow hidden addresses or operate entirely on service-zone logic.
Moreover, platforms that map service areas or allow radius-based entries are ideal for SAB SEO. Consistency in platform choice makes search engines interpret your business footprint correctly.
Citations for service-area businesses should not be posted on generic directories that prioritise physical presence over service reach. These can create ranking drag or visibility gaps.
Using specialised local citation services helps in identifying the most reliable SAB-compatible platforms while minimising manual effort.
B. Build a Service-Area Identity That Search Engines Can Read
SABs covering multiple territories need structured representations.
Generally, experts create city-level descriptors that match searcher intent, such as “plumbing services near [city]” or “commercial cleaning [metro area].”
They also maintain identical service-area data across every listing. Multi-zone logic guarantees that engines recognise your footprint without exposing a private address.
This approach signals relevance in local SERPs and pushes topical authority for citations for service-area businesses.
Consistency also reduces duplicate content flags, which is a common issue when service zones overlap or are inconsistently listed.
C. Deploy the “Clean Citation Stack”
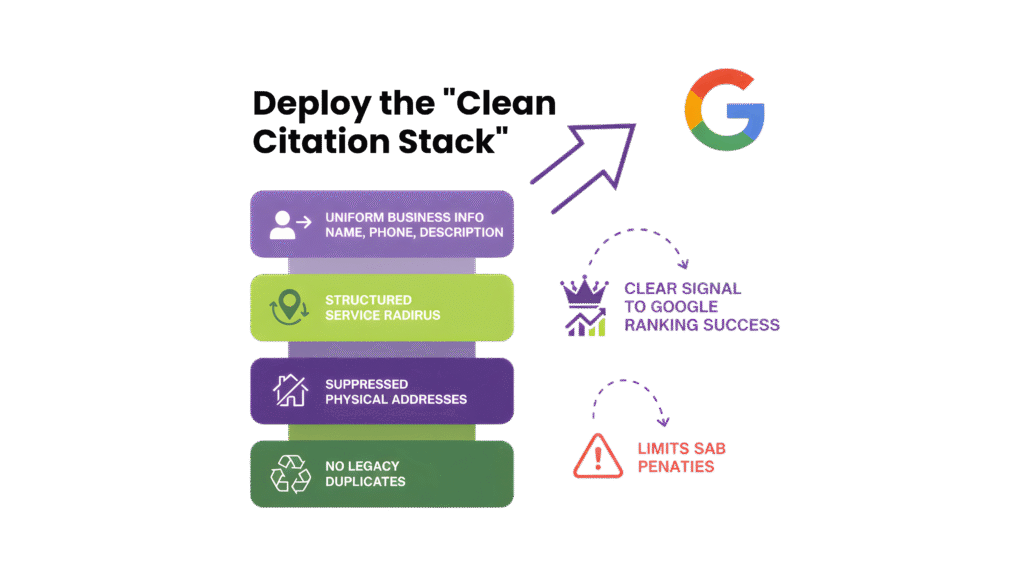
Standardisation is key here. It can be done by
- Using structured fields for service radius
- suppressing physical addresses
- removing legacy duplicates tied to prior addresses.
Every listing should present a uniform business name, phone number, and service description. This “clean citation stack” establishes a clear signal to Google, maps correctly to query intent, and limits potential SAB-specific penalties.
Partnering with a local SEO citation building service ensures these stacks remain error-free and replicable across hundreds of directories, saving operational overhead.
D. Align Categories and Narratives With SAB Behaviour
Categories influence discovery more than raw presence.
B2B businesses use service-based categories rather than location-based ones for their NAP setup. Then, local citation services map these categories to search queries such as “near me,” city-specific intent, or service-focused terms.
Brands and their sites should maintain uniformity across all platforms. Having a consistent category mapping reinforces the business’s topical footprint. It allows search engines to understand exactly which services are offered in each territory.
This also supports NAP setup alignment, further stabilising local rankings.
E. Add Secondary Validation Fields
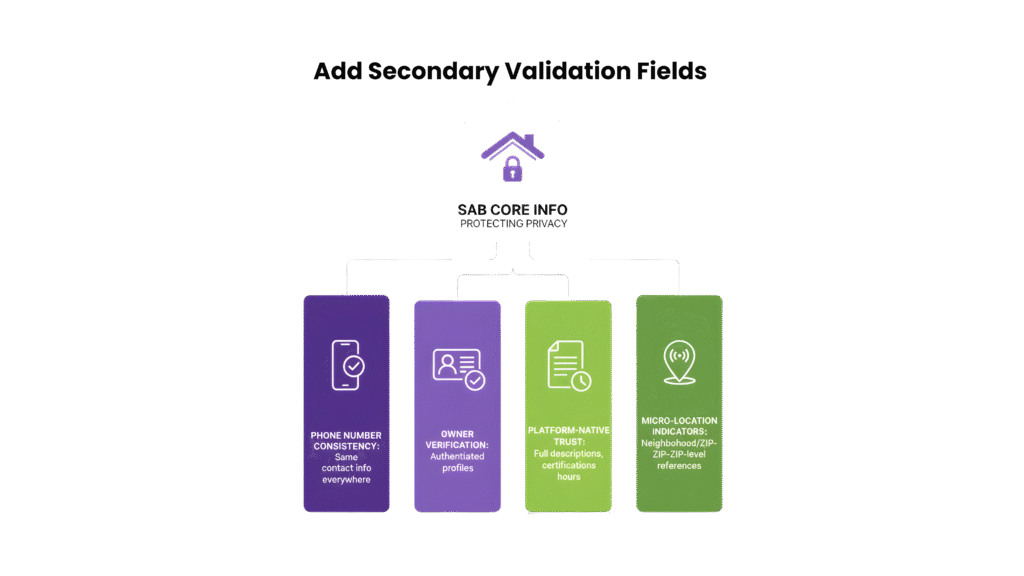
Validation fields strengthen trust and local search authority. They give search engines more signals without exposing addresses.
Secondary fields verify consistency, ownership, and relevance across platforms. Beyond core information, specialists should add elements that increase trust signals among high-intent clients.
Some examples are:
- Phone Number Consistency: Ensure every listing uses the same contact number for both tracking and verification purposes.
- Owner Verification: Platforms that require verified ownership confer an additional credibility layer, signalling authenticity to search engines.
- Platform-Native Trust Elements: Fill business descriptions, service notes, and territory markers fully. Include hours, professional certifications, or industry affiliations when applicable.
- Micro-Location Indicators: Even without a physical address, leverage neighborhood or ZIP-level references to reinforce local relevance.
These secondary signals strengthen the link between your SAB listing and real-world business legitimacy, which helps Google prioritise your business in map packs.
F. Track Ranking Impact Without Relying on Links
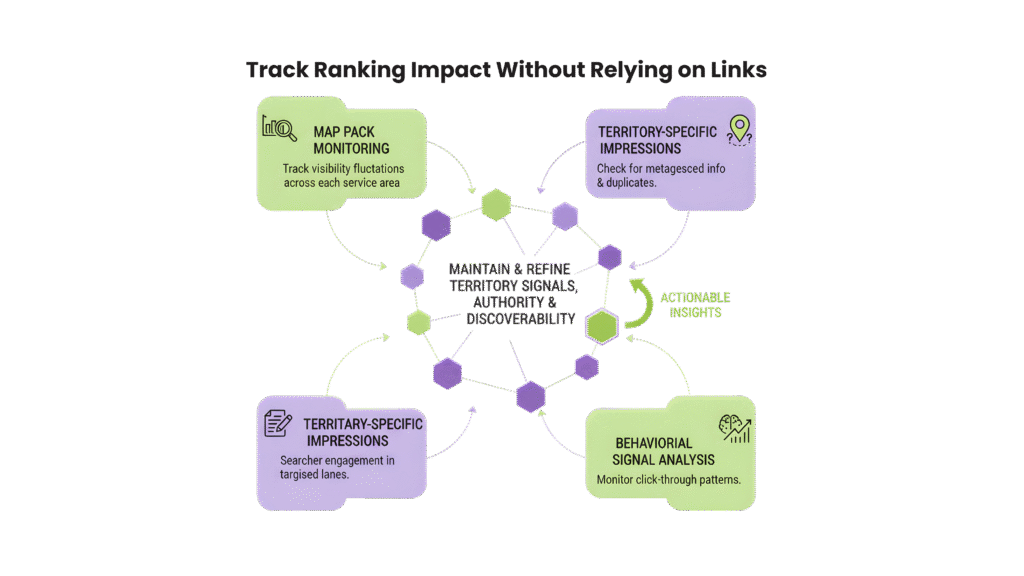
Citation performance cannot rely on backlinks alone. SAB visibility needs territory-focused, trackable signals.
Tracking ensures listings maintain authority and discoverability over time.SAB citation strategies are measured differently. Track:
- Map Pack Monitoring: Track visibility fluctuations across each service area.
- Territory-Specific Impressions: Correlate listing activity with searcher engagement signals in targeted zones.
- Citation Consistency Audits: Regularly check for mismatched information, duplicate listings, or suppressed data that might hurt SERP presence.
- Behavioral Signal Analysis: Monitor click-through patterns from map listings to verify which zones convert best.
Tools focused on SAB SEO allow monitoring without needing backlinks, enabling actionable insights to maintain and refine territory signals continuously.
Following this roadmap allows service-area businesses to build structured, compliant citations without exposing private addresses. By syncing platform choice, service-area representation, and category mapping with secondary validation, you can generate lasting local SEO visibility.
These citations work as reliable ranking signals for map packs and organic search. They also offer a strong foundation for organic link building and a sustainable local authority.
Conclusion
Search engines reward local citation services that maintain their NAP setup and SAB SEO hygienically when it comes to citation building for service-area businesses.
Local SEO citation building services should define their clients’ territories clearly, maintain consistent service data, and respect platform rules around hidden addresses.
Citation building can stabilise rankings across cities, reduce identity conflicts, and reinforce trust signals that algorithms rely on to map service intent. For brands operating without a physical storefront, designing citations that behave like structured location metadata is a priority.
They must be precise, repeatable, and aligned with local algorithms service boundaries. This disciplined approach provides for address-free businesses to still compete, rank, and earn local visibility under competitive conditions.
FAQs
How do citations help service-area businesses rank without a physical address?
Citations give Google stable signals when an address isn’t visible. Consistent NAP formatting shows operational legitimacy. Clean profiles reduce confusion across mapping data. Search engines rely on this stability to understand service boundaries and match you with real-world demand.
Which citation sites work best for service-area businesses?
The best platforms are those that support hidden addresses and structured service areas. Industry sites help with relevance. High-trust directories strengthen authority. The goal is to present one clear version of your business so Google can map you to local demand signals.
Do service-area businesses need NAP even if the address is hidden?
Yes. Google still needs a stable internal record. Hiding your address only affects what users see. It doesn’t remove the need for consistent business data across platforms. Consistent NAP gives algorithms the confidence to rank you for location-driven queries.
How does inconsistent NAP formatting affect SAB rankings?
Inconsistency breaks Google’s confidence. When signals differ, rankings flatten. SABs rely more on profile clarity because they lack physical anchors. Tight NAP structure sends a clean trust signal and removes friction in location validation.
Do citations still matter if an SAB focuses heavily on reviews?
Yes. Reviews help persuasion, not structural trust. Citations create baseline confidence in your business data. Together, they build a profile that’s easy for Google to interpret and comfortable for users to trust.
- Your cart is empty Browse Shop
DISCUSS NEW PROJECT OR JUST TO SAY HELLO GET IN TOUCH WITH US
info@Fastlinko.com
+91-9990725969
200 Park Home Avenue
M2R 1A2 North York, ON, Canada
© Fastlinko 2025 . All rights reserved, Rankfast







